描述
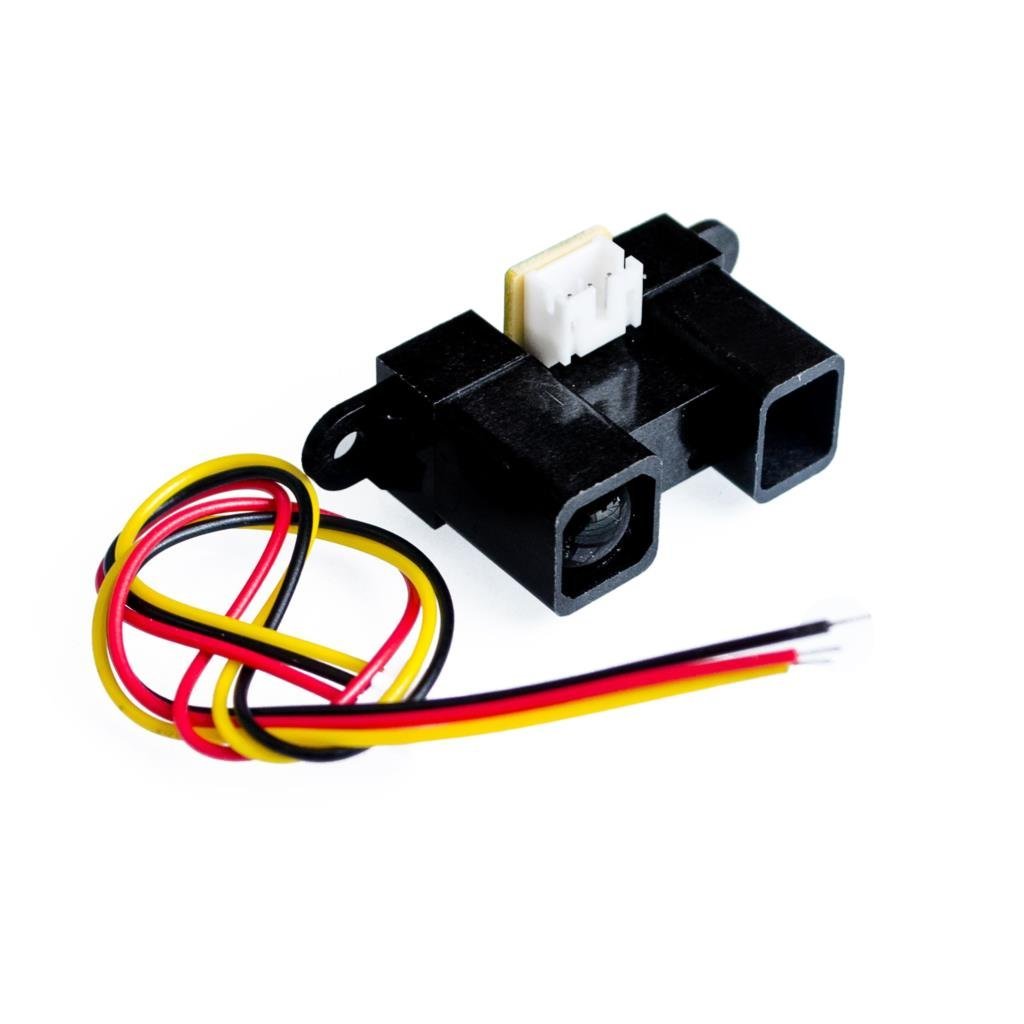
SHARP GP2Y0A21YK0F 紅外線距離感測器 測量範圍 10~80cm Analog 夏普測距感測器
台灣智能感測科技官網, 購買 更多關於 analog, GP2Y0A21YK0F, IR-紅外線距離感測, IR紅外線近接, IR紅外線近接測距, Sharp, 夏普, 測距, 紅外線, 距離, 距離傳感, 距離感測, 距離感測模組, 的產品
SHARP GP2Y0A21YK0F 紅外線距離感測器 測量範圍10~80cm Analog 夏普測距感測器
SHARP GP2Y0A21YK0F 紅外線距離感測器 是為機器人或任何其他項目添加避障或動作感應的好方法。 GP2Y0A21YK0F 檢測距離為4“至32”(10厘米至80厘米),模擬電壓指示距離,該傳感器非常易於使用。GP2Y0A21YK0F 紅外線距離感測器 是一種距離測量傳感器組件,由一個PSD (位置靈敏感測器)、IRED(紅外發光二極管) 和信號處理電路組成, 採用三角測量法:檢測距離不易受到,各種物體反射率,對環境的溫度和持續操作時間的影響。輸出的電壓對應檢測距離。因此,這種感測器也可以用來作為接近感測器
GP2Y0A21YK0F 夏普距離傳感器是許多需要精確距離測量的項目的流行選擇。這种红外傳感器比聲納測距儀更經濟,但它比其他紅外線替代品具有更好的性能。與大多數微控制器的接口非常簡單:單個模擬輸出可以連接到模數轉換器以進行距離測量,或者輸出可以連接到比較器以進行閾值檢測。該版本的檢測範圍約為10厘米至80厘米(4“至32”)。
功能摘要
- 工作電壓:4.5 V至5.5 V
- 平均電流消耗:30 mA(注意:該傳感器以較大的短脈衝串提取電流,製造商建議在電源附近放置一個10μF或更大的電容,並靠近傳感器接地以穩定電源線)
- 距離測量範圍:10厘米至80厘米(4“至32”)
- 輸出類型:模擬電壓
- 距離範圍內的輸出電壓差異:1.9 V(典型值)
- 更新周期:38±10毫秒
- 尺寸:44.5mm×18.9mm×13.5mm(1.75“×0.75”×0.53“)
- 重量:3.5克(0.12盎司)
 |
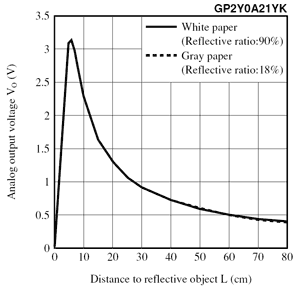
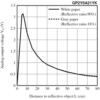
線性化輸出
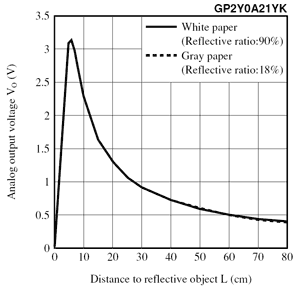
傳感器輸出電壓與測量距離的倒數之間的關係在傳感器的可用範圍內近似線性。所述GP2Y0A21YK數據表(374K PDF)包含模擬輸出電壓的曲線圖作為距離的倒數的到反射對象的函數。您可以使用此圖通過構建將輸出電壓(V)的倒數與距離(cm)相關的最佳擬合線來將傳感器輸出電壓轉換為近似距離。在最簡單的形式中,線性化方程可以是與反射物體的距離近似等於恆定比例因子(〜27V * cm)除以傳感器的輸出電壓。添加一個恆定的距離偏移量並修改比例因子可以提高這條線的擬合度。
Arduino 範例碼
int IRpin = 1; // analog pin for reading the IR sensor
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // start the serial port
}
void loop() {
float volts = analogRead(IRpin)*0.0048828125; // value from sensor * (5/1024) - if running 3.3.volts then change 5 to 3.3
float distance = 65*pow(volts, -1.10); // worked out from graph 65 = theretical distance / (1/Volts)S
Serial.println(distance); // print the distance
delay(100); // arbitary wait time.
}
Sharp GP2Y0A21YK0F Analog Distance Sensor 10-80cm
Feature summary
- Operating voltage: 4.5 V to 5.5 V
- Average current consumption: 30 mA (note: this sensor draws current in large, short bursts, and the manufacturer recommends putting a 10 µF capacitor or larger across power and ground close to the sensor to stabilize the power supply line)
- Distance measuring range: 10 cm to 80 cm (4″ to 32″)
- Output type: analog voltage
- Output voltage differential over distance range: 1.9 V (typical)
- Update period: 38 ± 10 ms
- Size: 44.5 mm × 18.9 mm × 13.5 mm (1.75″ × 0.75″ × 0.53″)
- Weight: 3.5 g (0.12 oz)
 |
Linearizing the output
The relationship between the sensor’s output voltage and the inverse of the measured distance is approximately linear over the sensor’s usable range. The GP2Y0A21YK datasheet contains a plot of analog output voltage as a function of the inverse of distance to a reflective object. You can use this plot to convert the sensor output voltage to an approximate distance by constructing a best-fit line that relates the inverse of the output voltage (V) to distance (cm). In its simplest form, the linearizing equation can be that the distance to the reflective object is approximately equal to a constant scale factor (~27 V*cm) divided by the sensor’s output voltage. Adding a constant distance offset and modifying the scale factor can improve the fit of this line.
Alternative Sharp distance sensors
We have a variety of Sharp distance sensors to choose from, including the shorter-range (4 – 30 cm) GP2Y0A41SK0F and longer-range (20 – 150 cm) GP2Y0A02YK0F. These analog distance sensors have similar packages and identical pin-outs, making it easy to swap one version for another should your application requirements change. We also carry the newer Sharp GP2Y0A60SZ analog distance sensor (10 – 150 cm), which outperforms the other analog Sharp distance sensors in almost all respects, offering a low minimum detection distance, high maximum detection distance, wide 3 V output voltage differential, high 60 Hz sampling rate, operation down to 2.7 V, and optional enable control, all in a smaller package.
Dimensions
| Size: | 1.75″ × 0.75″ × 0.53″ |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 3.5 g |
General specifications
| Maximum range: | 80 cm |
|---|---|
| Minimum range: | 10 cm |
| Sampling rate: | 26 Hz |
| Minimum operating voltage: | 4.5 V |
| Maximum operating voltage: | 5.5 V |
| Supply current: | 30 mA |
| Output type: | analog voltage |
| Output voltage differential: | 1.9 V |
Notes:
- 1
- Typical; can be as low as 21 Hz.
- 2
- Average; this sensor draws current in large, short bursts, which is why it is recommended a 10 µF capacitor or larger be placed across power and ground close to the sensor.